Links
Report of search
Abstract
Library
About Malta
Department
Faculty
DonNTU
Abstract of masters work
Subject: "Vector control systems with state observers"
Historically, the direct current was the most widespread and widely applied for electric motors in the sphere of manufacture, down to the end of the 20th century. It has been caused first of all by high efficiency, the rigid mechanical characteristic and a wide range of frequencies of rotation which could be regulated. The machines using an alternating current traditionally lost on these parameters, and were used at less important installations , which did not demand a high accuracy of the regulation.
But since recent time, the science has made great progress by way of semiconductor elements and microprocessor devices. A huge base for perfection of control systems for AC drives has appeared due to this. It becomes possible to create controlled drives based on others regulation laws.
One of the most perspective principles is vector control. It has been formulated in the beginning of 70th years of XX century in F.Blashke's works. The idea is that the vector control system is oriented on the vector of rotor's magnetic flux linkage. Thus the moment of engine is oriented on the transversal constituent of vector of stator current, and a magnetic stream is a longitudinal constituent. It allows to organize the management of engine similar to the engine of direct current, and also get similar dynamic descriptions at the frequency control.
On animation for simplicity the changes of projections of rotor's magnetic flux linkage vector on the stator systems of co-ordinates are shown.
The vector control systems have AD high stability and not sensitive to the external factors. It make their wide application in industry, where they will maximally realize the consumer properties. Different laws of optimum control are easily realized.
For creation of precision and high-speed system, the principle of the subordinate regulation on several coordinates (magnitudes) of the motor is used as a rule. In the given system it can be a stator current, speed of rotation of a rotor and magnetic linkage. Last magnitude can be estimated indirectly through values of currents, voltages and frequency of rotation of orthogonal system of co-ordinates.
The purpose of my work is system engineering of vector control without a physical feedback on speed that allows to exclude the tacho-generator and, accordingly, to raise reliability of the electric drive.
The scientific novelty of work consists in development of a new control method of the asynchronous motor without application of speed sensor on the basis of state observer. Different variants of quality improvement of evaluation of signal, which can be used in similar control systems, are offered.
As a result of the carried out work it is planned to create automatic vector control AD system without the speed sensor, astatic on loading. Thus its dynamic characteristics will not yield to similar systems with a sensor and PI-regulator of speed.
Review of existent researches and developments:
I. Master's degree work Bondarenko E.A. : "Development of vector control system by the asynchronous electric drive with the state observers". Construction of the system with the use of a regulator of the dynamic moment is offered. «During performance of work the vector control system of the asynchronous motor with the state observers, which settles to provide the astatic systems on loading without diminishment of its fast-acting, was explored. The basic results of the work are following:
1. The developed mathematical model of the asynchronous motor with a short-circuited rotor in the orthogonal system of coordinates, oriented on the vector of rotor's magnetic flux, which is used for research of static and dynamic characteristics of the motor, and also at designing of the vector control system.
2. The grounded expedience of adjusting of dynamic moment with a purpose is the increase of astaticism on loading, and the synthesized regulators of the proper vector control system with maintenance of permanent of rotor's magnetic flux. The channel of adjusting of rotor's magnetic flux (regulator of longitudinal constituent of stator current and regulator of rotor's magnetic flux) and channel of adjusting of speed (regulator of dynamic moment and regulator of speed ) are synthesized.
3. Different variants of state observers of complete order (in relation to the object of supervision) are synthesized, that allow to restore a signal of the dynamic moment: the first and second order, and also two variants of observers of the third order (on the basis of complete model of object of adjusting of the channel of speed and on the basis of the curtailed model of a contour of adjusting of dynamic moment). It is set that that on the part of simplicity of technical realization more effective is the first and last from the listed state observers, which have been synthesized.
4. Static and dynamic descriptions of the vector control system with the state observers and also influence of the last on these characteristics are appraised. It is ascertained that the difference of dynamic properties (dynamic error and presence of swaying), which, nevertheless, is very insignificant even in transient operating modes , increases together with increase of observer order. Application of each of the developed state observers is perspective for an estimation of the dynamic moment with the purpose of increase astaticism of the vector control system.
5. The possibility of application of state observers with permanent coefficients at the two-zone adjusting of speed is appraised. It is ascertained that their application is fully possible and effective, as it results in the insignificant improvement of dynamic properties of the vector control system in dynamic modes.»(http://masters.donntu.ru/2005/eltf/bondarenko/diss/index.htm).
II. Development NTTSE «Vector» «ADAPTIVE VECTOR CONTROL SYSTEM of the ASYNCHRONOUS ELECTRIC DRIVE»
«1.A new series of asynchronous electric drives with vector principles of control, possessing the functions of adaptation to parameters of rotor circuits, mechanical part of drive, dynamic non-ideal inverting and autotune of parameters of a control system on parameters of power channel of a drive is developed. The electric drive is oriented on application for control of mechanisms and technological processes showing increased requirements to dynamic characteristics and a range of regulation of speed.
2.The represented algorithm of compensation of the non-ideals of voltage inverter, has allowed to minimize influence of delays of switching and a "dead" zone in commutations the top and bottom keys of a phase on accuracy of the task of a stator voltage and, as a result, to lower pulsations at small levels of speed and extend the range of its adjusting.
3. The algorithm of autotune of parameters of the control system, realized as an option, allows on the basis of formation in a drive of the special test modes, realized by exceptionally internal facilities of drive, automatically to determine active resistance of stator and rotor, inductance of the magnetization, equivalent inductance of stator dispersion, moment of inertia of a drive and on their basis to expect all parameters and coefficients of the vector control system.
4.The offered algorithm of adaptation to change of parameters of a mechanical part of the drive, realized as an option, allows to carry out the primary tuning of the control system at the moment of inertia of a drive in thespecial test operating mode, and also calculate the moment of inertia and the moment of loading in an ordinary mode of operations of a drive, providing the proper tuning of the control system. This algorithm can be the autonomously-realized part of algorithm of identification and control of multimass nonrigid mechanical system.
5.The algorithm of adaptation to the temperature change of a constant of time of a rotor allows to estimate size Tr and Rr on the basis of interrelation between rotor's magnetic flux and the instant reactive AD power, calculated on voltages and currents of a stator, and also to execute tuning of parameters of a control system by results of these estimations. The invariance of characteristics of a drive to change Rr is provided as a result. The algorithm is simple in realization, unsensible to Rs , does not require information about speed of rotor, is efficient down to zero speed.»(http://vectorgroup.ru/articles/article4)
III. «Vector control system without sensors with orientation on a vector of rotor's magnetic flux » Authors: Dar'enkov A. B., Markov V. V., Tytov V. G. Nigegorodsky state technical university.
The brief analysis of quality of evaluation of a required signal depending on an interval of discrete is carried out.
IV. «Systems of indirect speed adjusting with the state observers» Authors: Tolochko O.I., Piskovatskaja O.V. , Kudokocev S.M. , Donetsk national technical university.
The analysis of two variants of state observers with reference to a direct current motor is carried out in this article, the method of adjustment of the observable signal of speed up to the actual, real value by calculation of a static current and an institution of the proper correcting communication on the entrance of the system is offered. The idea can be successfully used in similar systems, in particular, in vector control.
There are the mathematical models of AD, which allow to make system without the sensor of speed, calculating its current co-ordinate actually on mathematical description of motor, but their exactness and range of adjusting of speed get worse here. Construction of state observer is the second variant of renewal of co-ordinate of speed, the synthesis of which will be described in this work. It is achieved the most exact renewal of co-ordinate by the synthesis of observer of minimum order. But in practice it appears it is not quite justified from the necessity of application of additional devices for measuring of entrance or correcting signal.
Construction of state observer of a complete (3th) order is described in this work, the entrance of which there is the task of voltage on thyrystor converter (output of a regulator of current). Frequency of rotation is the main observable coordinate. Correcting communication is carried out on the state variable of current. At construction of model of the observer a contraEMF was taken into account, which has made the closed contour, thus having provided observability of object. The coefficients of correcting feed-backs were calculated, having choosen for desired polynom Battervort.
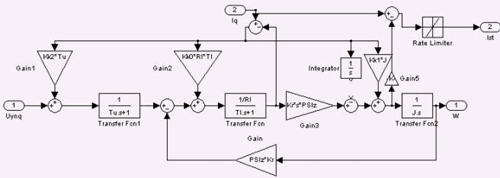
Fig.1. Model of state observer with identification of a static current.
For modelling the concrete motor was chosen: MTK-12-6. At closing of the system on own coordinates and control of observable speed, occurrence of an error between actual and observable speed equal of 20% is observed.
As a result of carrying out of researches 3 ways of elimination of a mistake have been determined:
1. Selection of own frequency of the observer w0. For given system optimum value appeared 2/Tu, where Tu- constant of time of thyrystor convertor. An error has made 0%.
2. Addition of additional integrator in model of the observer. The integrated size is the difference of currents of motor and the observer. The output of the integrator is summarized with with the moment of the motor. It also has allowed to liquidate completely an error, the fast-acting of the system has not worsened.
3. Identification of a static current and its institution on an input of system. This method allows to construct system astatic on loading.
Application of a combination of 1th and 2th methods gives practically ideal conformity of observable and actual speed.
Results are represented on Fig.2,3. Where : 0- own speed, 1- w0=2/Tu, 2 - w0=1/Tu integrator is applied. 3 - w0=1/Tu, without integrator.
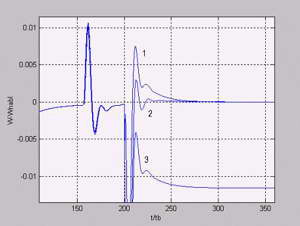
Fig.2. Graph of dependence of error of speed evaluation from the rationed time in a vicinity of loading imposition.
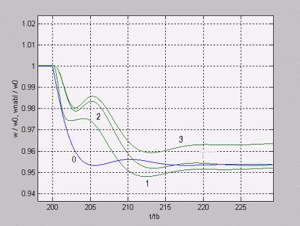
Fig.3. Graph of dependence of the rationed actual and looked after speed from the rationed time in a vicinty of loading imposition.
Proceeding from results of research, it is possible to make a conclusion on practically possible application of this model of observer for exact identification of speed in the vector control AD systems.
In the case of requirement of the astaticism system on loading calculation of a static current and its institution through the Kis coefficient, equal to the relation of falling of speed in the system closed on observable coordinate to falling speed in the broken system on an input of regulator of current straight or on the input of regulator of speed with a coefficient reverse to it, is used. Dynamic properties of such system are represented on the figures 4,5. Thus the system is closed on observable speed.
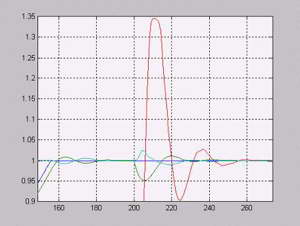
Fig.4. Dynamic characteristics of motor in a vicinity of loading imposition.
On Fig.4. a current is marked red, green is speed.
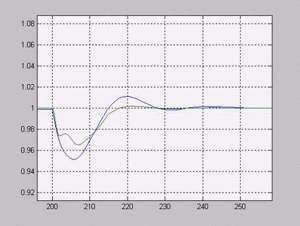
Fig.5. Exactness of evaluation of speed in vicinity of loading imposition.
On Fig.5. the dark blue shows actual speed, green is looked after.
Though the received results can be named satisfactory, however much the improvement of quality of transitional processes will be direction of my further activity, in particular, reduction of overshoot and swaying. The further analysis of existing and search of another ways of removal of evaluation error and possibilities of construction of the astatic system will be also conducted.
Autobiography | Links | Report of search | Abstract | Library | About Malta