Actuality of theme
The theme of master's work is “System determination of hardness of water of the systems of heatings ”
on the basis of measuring of specific conductivity. I see actuality of the chosen theme in tom, that
from data of conductivity it is possible to judge waters about hardness, and it in same queue enables
to define quality of water for the system of heating. As to water great demands are made, it is necessary
to ground whether preliminary preparation of water is needed or not. Preparation of water - physical and
chemical treatment of water, eliminating or substantially reducing еducation form and corrosion of heating engineering equipment . The oxides of iron can appear as a result of corrosion everywhere: internal corrosion of steel radiators, cast-iron or steel caldrons quite often results in the accumulation of the core boring in the underbody of radiators, and also in valves, valves and pumps. It not only diminishes heat emission of heatings devices but also creates obstacles for a water-course in the system, from what its falls KPD and advantages, tied-up with the use of regulative devices, are lost. Therefore preparation of water is inalienable part of the modern heating engineering system. Any technological process of preparation of water is influence on podpitochnuyu or network water, causing purposeful change objective physical and chemical properties of water.
Purpose and tasks of work
The purpose of master's work is development of the system of determination of hardness of water of the systems of heatings from data of conductivity. On the basis of the got results it is necessary to ground the method of umyagcheniya of water, its complex preparation of water.
To the tasks it is possible to take followings:
- construction of mathematical model of measureable environment;
-research of temperature dependence of hardness of water, and also dependences of hardness ot the concentration of salts of cut-ins.
Review of existent researches in area of problem of hardness.
The special value for the systems of heating, as be said before,
has the use of feed-in water of the proper quality. Water of the
centralized drinkable water systems is used as a rule, quality of which
is regulated Sanpin a 2.1.4.559. Drinking-water., GOST 2874.82 Water is
drinkable. Quality of water is regulated the indicated documents on a
number of quantitative indexes, such as microbiological, parasitology,
radiological and other Only on maintenance harmful matters 724 indexes
are rationed in a drinking-water.
The amount of in water permeates depends on their physical and chemical
properties, mineral composition, temperature, to time of contact with minerals and. TDS is measured in mg/l, that in gravimetric amounts equivalently to one part on million (parts per million, ppm). In obedience to operating sanitary-hygenic requirements, a drinking-water must contain no more than 2000 mg/l of permeates.
Total Hardness, TH
it is accepted to bind Concept of inflexibility of water to cations of calcium (Na2+) and in less degree magnesium (Mg2+). In actual fact, all bivalent cations in one or another degree influence on inflexibility. They co-operate with anionami, forming connections (salt inflexibilities) able to fall out in sediment. Univalent cations (for example, sodium of Na+) do not possess such property. Distinguish the next types of inflexibility. General inflexibility. Concernes the total concentration of ions of calcium and magnesium. It is a sum of carbonate (temporal) and uncarbonate (permanent) i hardness.
Carbonate hardness.
Conditioned a presence in water of
gidrokarbonats and calcspars (at pH>8.3) and magnesium. This
type of inflexibility is almost fully removed at boiling of water and named temporal hardness.
Method’s to do more soft water
This method is reduced by hardness of water without the change of
amount of electrolyte, cut-in in water. Substituting for ions, accountable for surplus inflexibility is thus carried out. In particular, substituted for the ions of calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) the ions of sodium (Na), that prevents formation of deposits of limes at heating of water, as unlike calcspars, formings a variable constituent of inflexibility and magnesium, the carbonate of sodium remains a cut-in in water at an enhanceable temperature.
variable hardness.
Thus, there is jigging on ionoobmennykh resins of ions,
otvetstvenykhza surplus inflexibility (in this case Ca++) a
nd dissolution of Na+ of ions.
Polifosfatatnaya treatment
This method allows for a time to «link» salt inflexibilities,
not giving them during some time to fall out as scum.
Polifosfaty possess ability to form connections with the
crystals of CaCO3, saving them in a state of suspensoids
and, the same, halting the process of their agregirovaniya.
However necessary it is to have because of, that this mechanism
is capable of working only at temperatures, not exceedings 70-75 °C.
At more high temperatures inclination takes place to to a hydrolysis
and efficiency of method goes down sharply.
The magnetic or electric conditioning
Under the action of the strong magnetic fields takes
place modification of crystals of salts, accountable
for variable inflexibility, as a result salt education form
grow into the melkodispersnyy core boring which is not put
aside on-the-spot and not inclined to formation of compact forms.
The similar phenomena take place at the use of electric digits,
reducing the capacity of falling out
in sediment salts for their unitization.
However to the present tense reliable enough
information, touching efficiency of work of similar
sort of devices, is absent, especially at high tempreture,
near to the boiling point.
Reverse osmose
In accordance with this method, water prokachivaetsya under
high pressure through a semi-permeable membrane with pores,
having a diameter less than 0,05 mkm. Most ions of cut-ins filtered
on a membrane. Depending on an in-use membrane and other descriptions
of the carried out process of filtration ot 90 to 98 % in water ions
of cut-ins retire. Achieving more high efficiency of demineralizatsii
here is problematic. Possibility of realization of process of reverse
osmose fully automatically, and also absence of necessity in the use
of chemical reagents is done him especially attractive in the examined aims.
A process is economical enough, consuming electric power in
an amount 1-2 eAo.?an on 1 i3 of the processed water. The cost of equipment constantly goes down in connection with multiplying the volume of his output due to permanent expansion of spheres of the use.
A reverse osmose, however, is vulnerable if the processed water
is very hard and/or contains plenty of mechanical contaminations.
In this connection for multiplying the term of service of in-use
membranes preliminary umyagchenie of water is frequently required
or her polifosfatatnaya treatment, or iaaieoiia/yeaeo?e?aneia
onditioning and filtration.
Planned own results
The volume of control of hardness of water of the systems of heating is supposed
by measuring of this index in somes points of controls: on signing on heating, in the
line of signup, on an exit from the system. To that end setting of sensors of
conductometries of specific conductivity is planned in the points of controls.
The sensor of specific conductivity is executed in the form of cylinder from
ceramics with the little temperature coefficient of expansion, electrodes are inflicted
as thin metallic strips. Two electrodes of such sensor are connected to the source of
variable tension, and from two other the values are taken off differences of potentials,
proportional conductivity of water.
Permittivity of water characterizes resistance a flowing electric current,
being dependency upon maintenance of in her electrolytes of cut-ins, which inorganic salts
serve as in natural water, mainly. increased substantial appearance depending on the concentration
of salts of cut-ins.
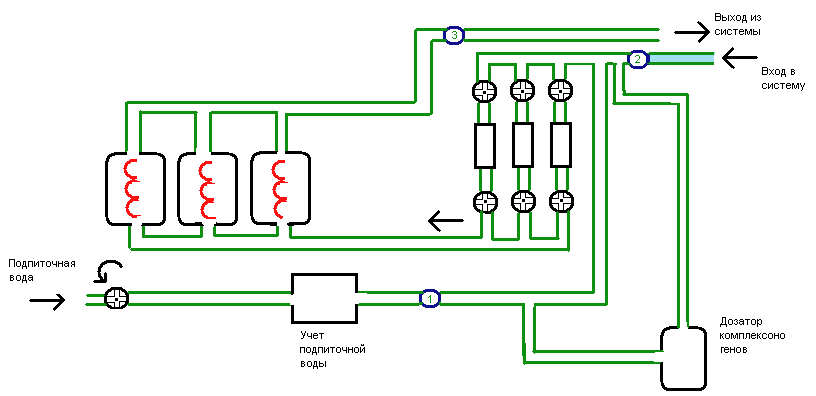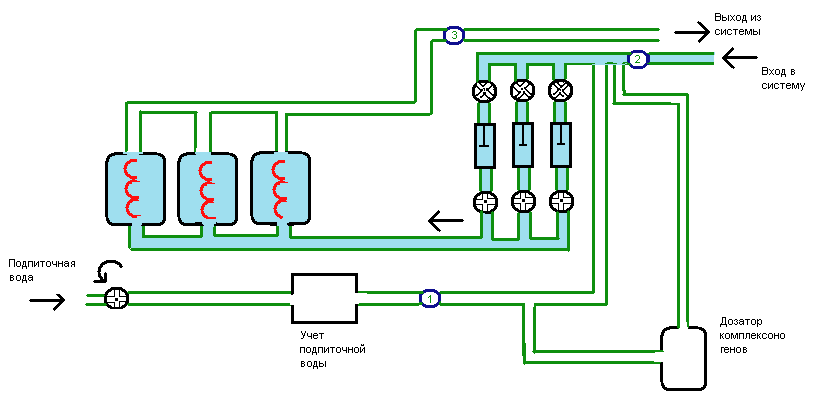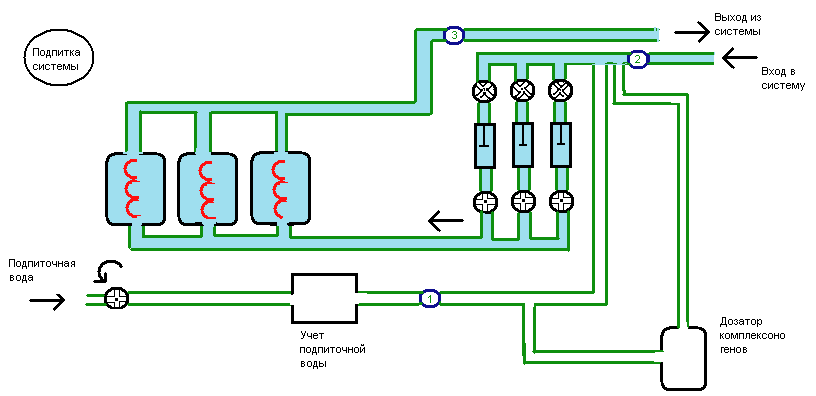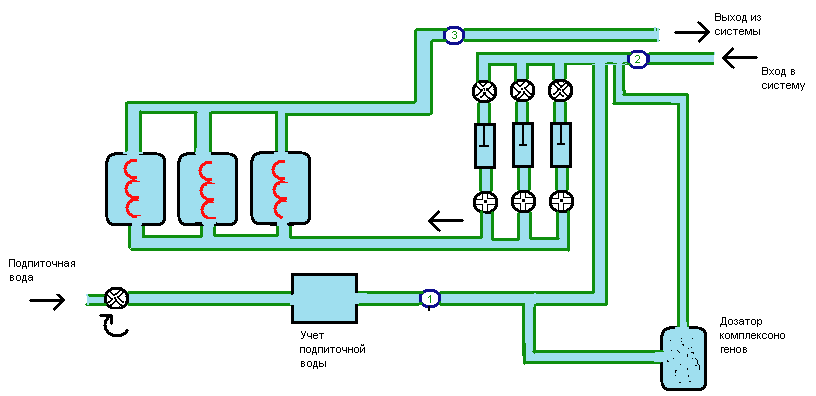
The hydraulic chart of the typical system of heating with pointing of points of
setting of sensors is presented on a picture 1:
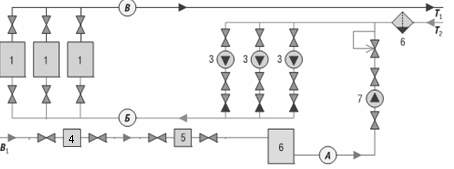
1- caldrons; 3 - are pumps of networks;4 it is a knot of account of waters for a signup;
5 - device of dosage of matters ;6 - a reservoir of supply of waters for a signup; 7 - signup pump .
A - point of selection of waters for a signup; Б - is a point of selection of test of network water; В- point of selection of test of network water.
Т1 - direct pipeline of network Т2- a reverse pipeline of the heating system
Literature :