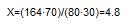
 |
|  ||
Master's portal of DonNTU
||
Master's portal of DonNTU

Faculty: Ecology and chemical technology
Speciality: hemical technology of high molecular connections
When creating simple industrial explosives on the basis of ammoniac saltpetre and dry fuel there is a problem of fuel application on the surface of oxidant and duration of firmness of distribution of these components. One of the ways to decide this problem is creation of glueing solution which contains both oxidant and fuel.
The purpose of this work is creation of glueing solution, which will provide the even distribution of combustible component on the surface of oxidant, and theoretical calculation of possible composition of compound of industrial explosive.
The composition of glueing solution is desirable to contain both oxidant and fuel, that is why it is necessary to solve the followings problems:
- to define composition of oxidants proceeding from their solubility. It is possible to do with the help of literary sources;
- to find component composition of glueing solution;
- to control chemical firmness of solution.
From the point of view of safety of finished goods and their efficiency for formation of explosive mixtures it is necessary to approach to the mixtures with zero or insignificant positive oxygen balance.
The surface of contact between fuel and oxidant is not developed enough. Thatís why the purpose of this work is finding the ways to solve this problem. Water-filled and emulsive explosives solve this problem by means of liquid component. But in this case it has many disadvantages. Above all it is short shelf life and large dependence on temperature. These disadvantages disappear, if a part of liquid component is decreased to the minimum. This means that the liquid must only come forward allegedly a thin shell which helps the even distributing of fuel for the surfaces of oxidant (a fuel dispergates), and, in one the time, to glue together both the component.
To achieve the purpose of this work it is necessary for glueing solution to meet the following requirements:
- not to be toxic;
- to have good water resistance;
- not to be an inert addition, that means it must increase the power indexes explosives;
- not to give fragile film.
To increase the power features of explosive to be developed, water (in composition of glueing solution) is substituted for solution of saltpetre, which serves as oxidant. Therefore, the necessary stage of work is determination of types of saltpetres with a maximal value at mutual dissolution.
It is set during the study of solubility of ammoniac and calcium saltpetres, that saltpetres do not influence on mutual solubility, it allows to use the mixture prepared beforehand.
According to the data obtained, the following chart was constructed [1]. Taking into account the cost of calcium saltpetre, which exceeds the cost of ammoniac saltpetre, the composition with percent content 70/30 % of ammoniac and calcium saltpetres is optimum for making fallopian. It has a high solubility which is 288 g in 100 ml of H2O.
To study the firmness of solution it was done the analysis of determination of pH solutions with an interval of three months. Data for determination of closeness of proper solutions were given.
Data obtained for pH solutions showed small decrease of pÕ (about 0,4%) in 3 months of stand. It does not influence essentially on chemical firmness and explosive indexes, and it is insignificant at storage of standards.
The addition of stiffener promotes glueing of oxidant and fuel in uterine solution. The most common stiffeners are polyacrylamide and sodium salt of carboxylmetyl cellulose. The first one is hardly to dissolve in uterine solution at a room temperature; further experiments were conducted with Na carboxylmetyl cellulose.
When carrying out tests the results for solubility of Na carboxylmetyl cellulose in solution of ammoniac and calcium setzer in proportion 70/30 (table. 1) were obtained. According to the results it is possible to conclude, that the most optimum concentration of Na carboxylmetyl cellulose in uterine solution is 4.5 %.
Table 1 is Solubility of Na carboxylmetyl cellulose in different proportion to uterine solution
| % of Na carboxylmetyl cellulose | Solubility | Closeness |
| 3.0 | Complete | A small bodying is in comparison to uterine solution |
| 4.5 | Complete | ∆Jelly-like mass |
| 6.0 | Partial | So thick, that almost does not flow |
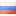
At first we define molecular proportion of mixture of ammoniac and calcium saltpetres [2]: , where X and Y are numbers of gram-atoms of ammoniac and calcium saltpetres, 80 and 164 Ėtheir molecular weight accordingly. We accept Y=1. Then:
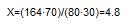 |
Such relation of molecules accords to the following percentage of mixture:
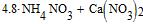 |
Letís define molecular relation of mixture of saltpetres and Na carboxylmetyl cellulose: 548X:269Y=95.5:4.5, where X and Y are numbers of gram-atoms of saltpetres and Na carboxylmetyl cellulose 548 and 269 Ė their molecular weight accordingly. Will accept Y=1. Then:
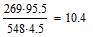 |
Such relation of molecules accords to the following percentage of mixture:
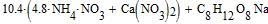 |
Having written the molecular relation of mixture, we find the amount of atoms of oxygen in mixture:
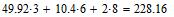 |
Amount of oxygen, necessary for combustion of mixture, we find from the equation:
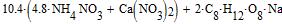 |
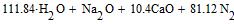 |
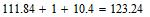 |
The amount of surplus of oxygen in mixture 228.19-123.24=104.92 atoms; expressed as a percentage:
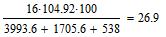 |
This calculation is computer-aided by means of the package of MathCad. MathCad package is created by constructors as an instrument for design engineers. It was created as powerful microcalculator, that allows to handle different engineering problems, such as algebraic problems and differential equation with of permanent and variable parameters, functions analysis, search of their extremums, numeral and analytical differentiation and integration, derivation of tables and charts at the analysis of the solutions obtained
Letís calculate the percentage depending on the thickness of glueing solution.
Letís construct the charts of dependence of percents AS and fuels in mixture on the thickness of glueing solution (pic. 1 Ė 2).
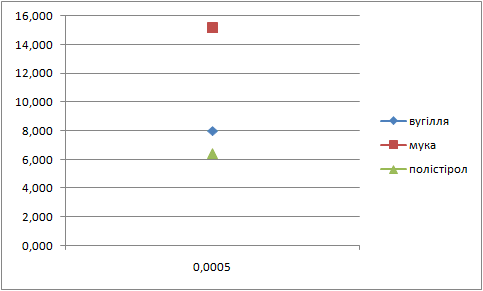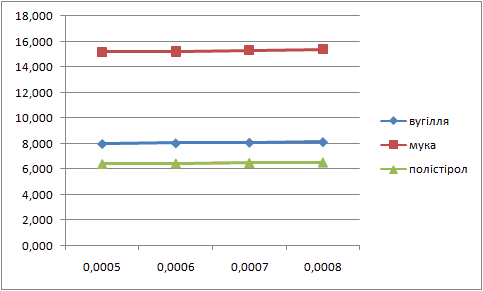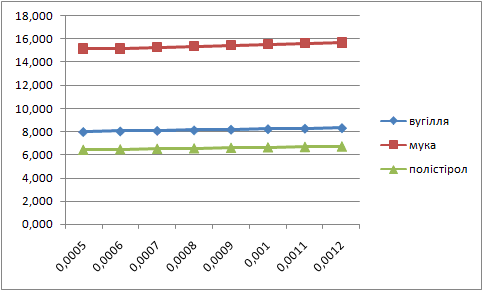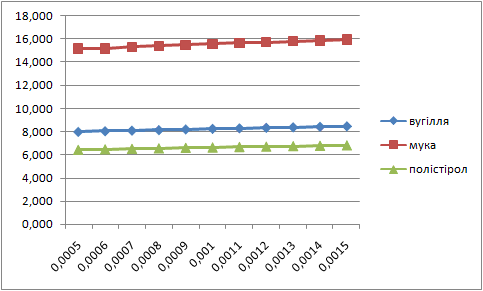 |
| Picture 1 - Dependence of the fuel percent in mixture on the thickness of layer of glueing solution(Animation 11 frames, 2 frames per second, 15 Íepeats) |
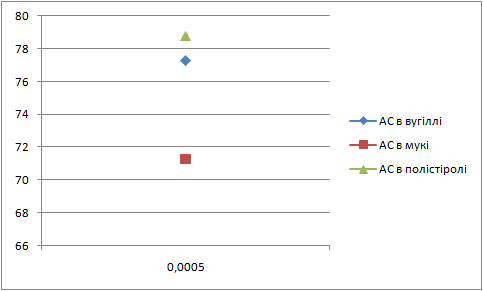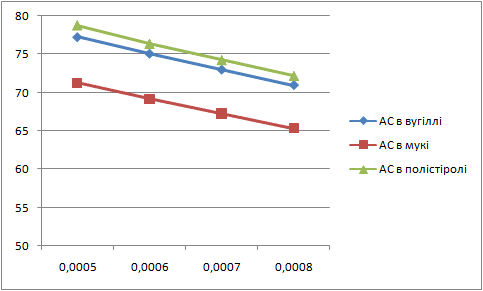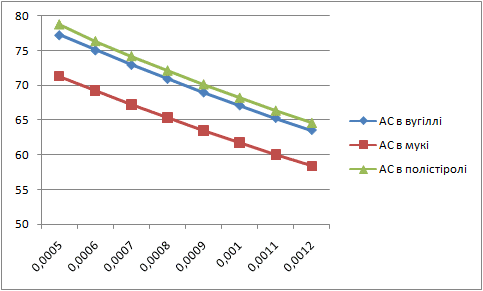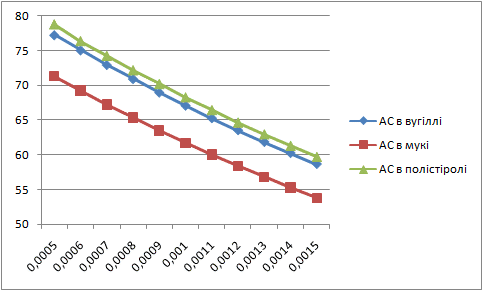 |
| Picture 2 - Dependence of ammoniac saltpetre percent in mixture on the thickness of layer of glueing solution(Animation 11 frames, 2 frames per second, 15 repets) |
Analysing these charts it is possible to conclude the following: the more the thickness of layer of glueing solution the more the percent of fuel in the mixture, and the less the percent of AS. Therefore it is necessary to take into account these dependences in the further research.
So, the results of our work are the following:The glueing solution to be developed includes the uterine solution of oxidant of ammoniac and calcium saltpetres ( it is determined by the the literary sources) and Na carboxylmetyl cellulose as a stiffener and fuel.
As a result of the experiments conducted, the following percentage of components of glueing mass is set: 4.5 % Na carboxylmetyl cellulose and 95.5 % pestle solution which consists of 70 % of AS and 30 % of calcium saltpetre. This composition has good glueing characteristics and shelf life not less than 3 months.
With the help of computer the dependence between percentage of industrial explosive to be developed and the thickness of glueing solution.